Definitions
Glass: Term for the actual material
Clear Glass: Mixture of silica sand and small amounts of alkaline salts such as lime, potash and soda.
Glazing: Process of installing glass in the framing as well as the process of installing the frame itself.
- However, can also refer to the glass that has been installed through this process.
Energy Efficient Glazing: Products that can reduce heat loss and/or heat gain through windows. Thereby reducing the energy needed to maintain a comfortable indoor air temperature (all without significantly reducing the visible light transmitted)
Safety Glass: Tempered or laminated glass that meets the testing requirements of 16 CFR 1201 (Code Of Federal Regulations)
Glass Types
Various glass types and definitions below. These are not glass types per se, but rather various definitions that have various overlap between them.
| Float Glass /Annealed Glass | Pouring molten glass into a bed of tin and letting it cool. Most of the glass produced in the US is float glass.Note: We will only use “Float Glass” as the term elsewhere on the site |
| Heat-strengthened Glass | Heating the glass to about 1100 degrees F and slowly cooling it.About twice the strength of Float Glass of the same thickness. This glass is used for places where the glass can be under cyclical wind pressures, or solar induced thermal stresses/expansions. |
| Tempered Glass | Subjecting Float Glass to a special heat treatment in which the glass is heated to about 1150 degrees F and then quickly cooled. The process is about 4 times stronger than float glass.Tempered glass is considered “Safety Glass”, so it can be used in hazardous locations as defined by the building code.If it breaks, it falls into a thousand of very small pieces rather than creating dangerous large shards. |
| Laminated Glass | Consists of two or more pieces of glass bonded together by an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral resin. When laminated glass is broken, the interlayer holds the pieces together even though the glass itself may be severely cracked. This type of glass is used where really strong glass is needed. Depending on make-up, it can be bullet resistant and provides high security against intentional or accidental breakage.Also considered safety glass and can be used in hazardous locations.Laminated glass also provides additional sound control. The additional thickness of glass provides extra sound control but the interlayer also helps dampen the otherwise rigid material allowing it to absorb sound better. |
| Tinted Glass / Reflective Glass / Heat-Absorbing Glass | Reflective Glass and Tinted Glass share a lot in common.Reflective Glass is coated with an extremely thin layer of metal or metallic oxide.Tinted Glass is produced by adding various colorants to the glass material.The purpose is to reduce the solar transmittance of the glass, which then would in turn reduce the air conditioning load of the building. It also helps reduce the brightness in the interior which means less fading of fabrics and carpeting.These glass types absorb heat (before transferring it into the building) and therefore if portions of it are in shade while portions in the sun, it can cause the glass to crack. Because of this, tinted glass is often heat strengthened or tempered to give it extra strength.Also reduces the amount of visible light let into the building, which is a negative. This means more artificial light is needed which will increase building operation costs and reduce energy efficiency.Within Insulating Glass, this reflective layer is placed on the inside of the exterior lite of glass. Its primary purpose is to save energy by reflecting solar radiation before it gets into the building. |
| Low-iron Glass | Iron oxide gives a light green cast to ordinary float glass. Low-Iron glass has a reduced amount of iron oxide, which gives it exceptional clarity, optimal light transmission, and excellent color transmission.Low-Iron glass is more expensive |
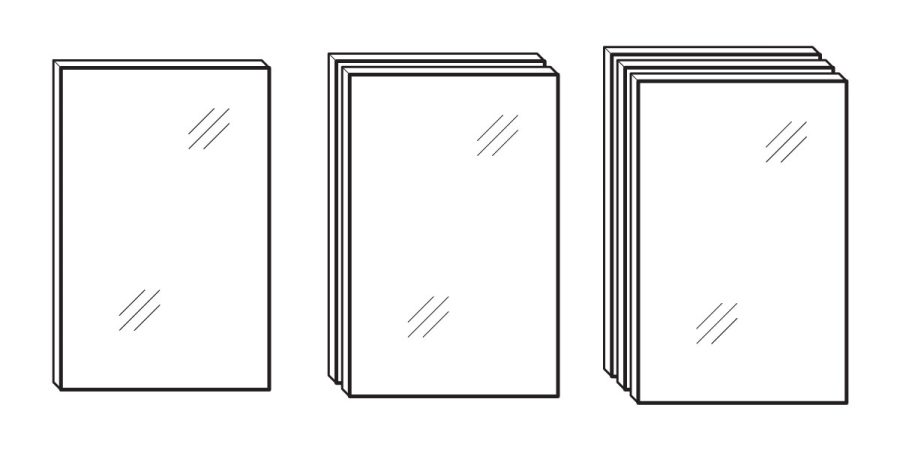
| Insulating Glass / IGU (Insulating Glass Unit) | Two or three sheets of glass separated by an air-tight sealed air space (this is referred to as hermetically sealed). Insulating glass has a much lower U-value than that of single-pane glass and is used almost exclusively in regions where heat loss is a problem.Can be made with any types of glass… both sheets could be float glass or heat strengthened, it just depends on the application. |
| Patterned Glass | Passes the sheets of glass through rollers on which the pattern is etched on one or both sides. Vision through the panel is diffused to a degree that depends on the pattern of the glass. |
| Wire Glass | Has a mesh of wire embedded in the middle of the sheet. The surface can be either smooth or patterned. Wire glass is used primarily in fire-rated assemblies of 45 minutes or less if it is not in a hazardous location.Despite the use of wire, it is not as strong as other common glass types and can present a hazard when broken.Wire glass cannot be tempered and does not qualify as safety glazing |
| Spandrel Glass | Spandrel glass has a permanently fused ceramic frit color to the back of heat strengthened or tempered glass. Spandrel glass is 100% opaque and typically used to conceal spaces of the building (like floor/ceiling structure in curtain wall construction)Normally manufactured and installed as a single sheet with insulation behind it. The insulation is normally pinned or taped into the frame.Sometimes confused with Shadow Box construction. |
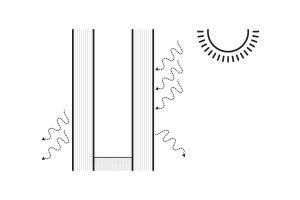
| Low-E /Low-Emissivity Glass | Selectively reflects and transmits certain wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. It is manufactured by placing an atomically thin coating of metal or metal oxide on the surface of a piece of glass or a thin film. This is done by bouncing metal electrons against the sheet of glass during fabrication.Low-E glass works by transmitting visible light and shorter wave solar radiation but reflecting the long-wave heat radiation from the air and warm objects.In cold climates: low-e glass admits solar heat gain during the day but prevents the built-up heat inside the building from escaping at night. In the summer the same glass will reflect much of the ambient long wave infrared heat away from the glass.In warm climates, low-e glass can be combined with tinted or reflective glass to prevent even more heat from being transmitted to the interior. |
| Electrochromic Glazing | Glazing that changes from opaque to transparent with the application of an electric current. When the current is on, the glass is transparent, when the current is off, the glass darkens or turns milky white, depending on its type.Never opaque, so it cannot always be used as privacy glass.Intended for control of light, ultraviolet energy, and solar heat gain.Can offer 20-30% of energy savings.The dimming capabilities can be utilized to help with very specific program requirements. For example, a computer lab might want selectively dimmed shading to provide reduced glare for screen time. |
| Suspended Particle Device (Spd)(Sim. To Electrochromic) | Uses a light-absorbing microscopic particle dispersed within a liquid suspension film, which is then sandwiched between two pieces of transparent conductive material.Appearance of the product can range from clear to partially darkened to totally opaque.Can be used for privacy or light and energy conservation.Can offer 20-30% of energy savings. |
| Polymer-dispersed Liquid Crystal Film(Sim. To Electrochromic) | Placing a polymer between the two pieces of glass (between laminated pieces of glass). Transparent to cloudy white is achievable. Translucent state offers total visual privacy but still allows a significant amount of light to pass through so it cannot be used for exterior light control. |
| Fire-rated Glazing | In addition to wire glass (45 mins or less typically), there are 4 types of glazing that can be used for fire glass. Fire-rated glazing is extremely expensive, and why you typically do not see curtain walls or glazing at the ground floor of fire egress stairs.Clear ceramic that has a higher impact resistance than wire glass and a low expansion of coefficient. Some do not meet safety glazing requirements, but there are laminated assemblies that are rated up to 2 hours and are rated for impact safetySpecial, tempered fire-protective glass. Two or three layers of tempered glass with a clear polymer gel between them. The gel is transparent under normal conditions, but under fire, the gel foams and turns opaque, slowing the passage of fire.Glass block. Not all glass blocks are rated, so it must be the glass block that is specifically fire rated. |