Architectural programming is essential for organizing project criteria and guiding design decisions. It emphasizes documentation, client communication, and problem identification, leading to better building functionality. The programming process consists of three phases, preparing for user needs and future changes, utilizing tools like affinity matrices for space relationships. Good programming ensures project success.
Photovoltaic systems (PVs) convert sunlight into electricity, utilizing semiconductor materials that generate DC electricity, which is then transformed into AC. PVs can be arrayed or integrated into structures and must comply with safety codes. They offer renewable energy benefits, but have high initial costs and require favorable locations for efficiency.
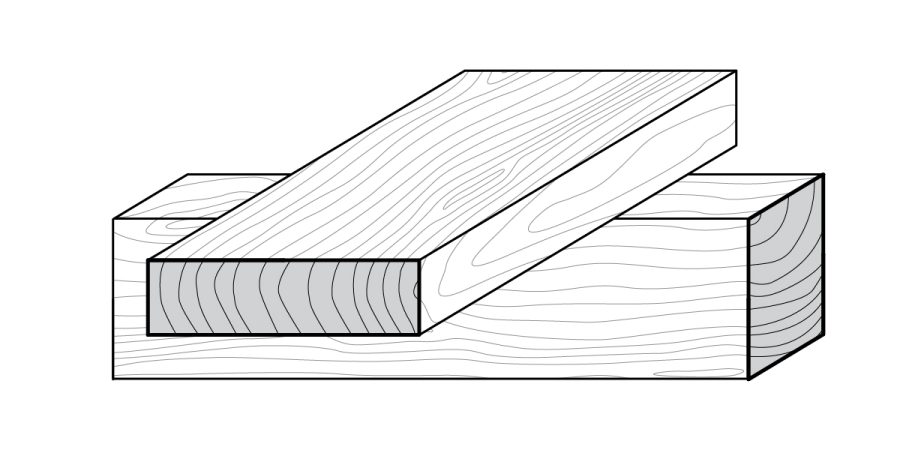
Heavy timber construction involves large solid timbers used for columns, beams, and planking, often combined with noncombustible materials for walls. Though one of the oldest building types in the U.S., heavy timber is largely being replaced by engineered mass timber due to cost and resource limitations. Both have distinct characteristics.
This content discusses communication systems, focusing on the differences between Local Area Networks (LAN) and Wide Area Networks (WAN). It explains terminal rooms, Building Automation Systems (BAS), security systems, access control methods, and site security strategies. The importance of balancing security with aesthetics while minimizing risk is emphasized throughout.
An Architect is expected to balance cost, function, time, and aesthetics of a project. In the past, there was never much thought to the sustainability of building materials, however, this […]
Introduction Sunlight is one of the most sought after components in a space, and codes are written to require access is provided to the resource. However, sometimes there is too […]
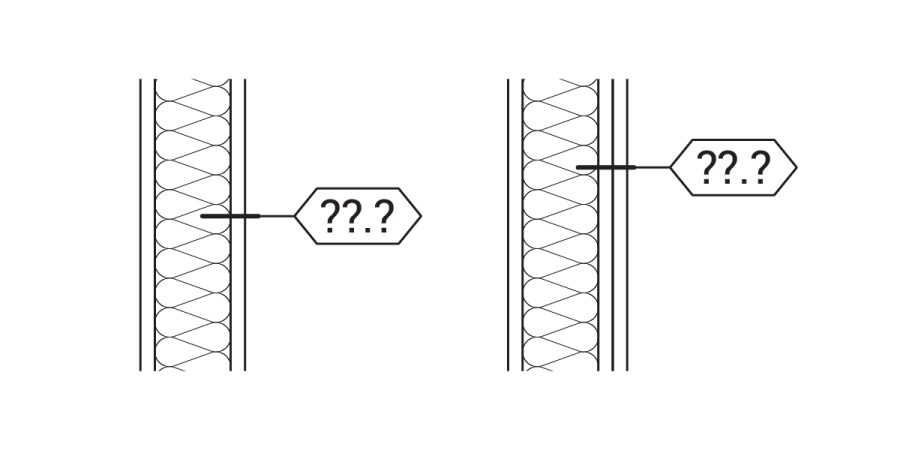
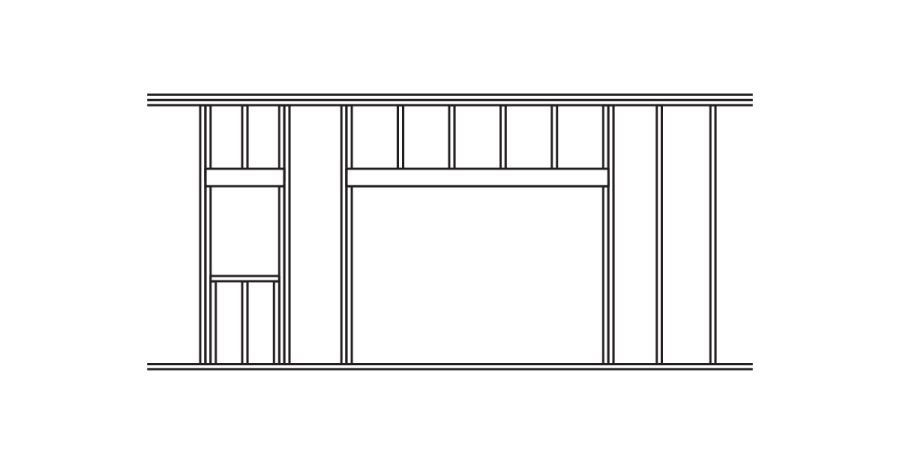
Introduction: Labeling interior partition wall types is a critical part to any construction documentation set. By using a wall tag/label, it allows you to convey a host of information that […]
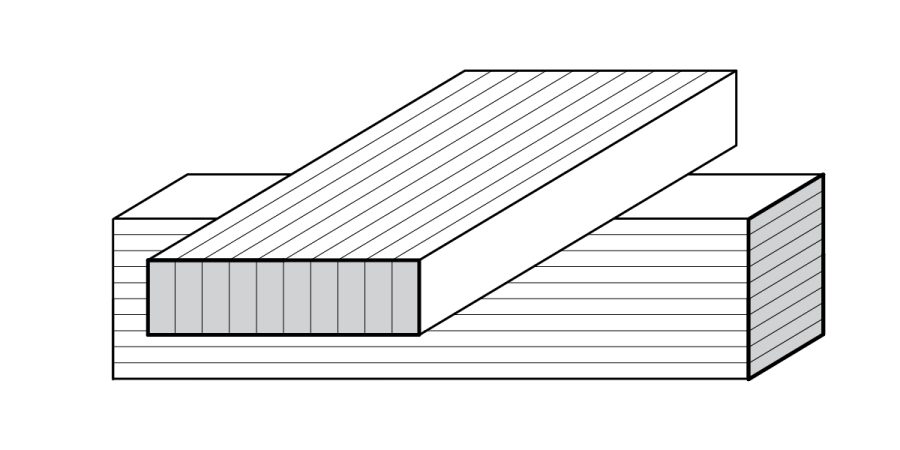
The content outlines various wood and framing terms, distinguishing between wood, lumber, and timber. It details light and heavy timber constructions, different framing types like balloon and platform framing, and explains structural components such as openings, firestops, sheathing, plywood, and engineered panels like OSB and MDF.
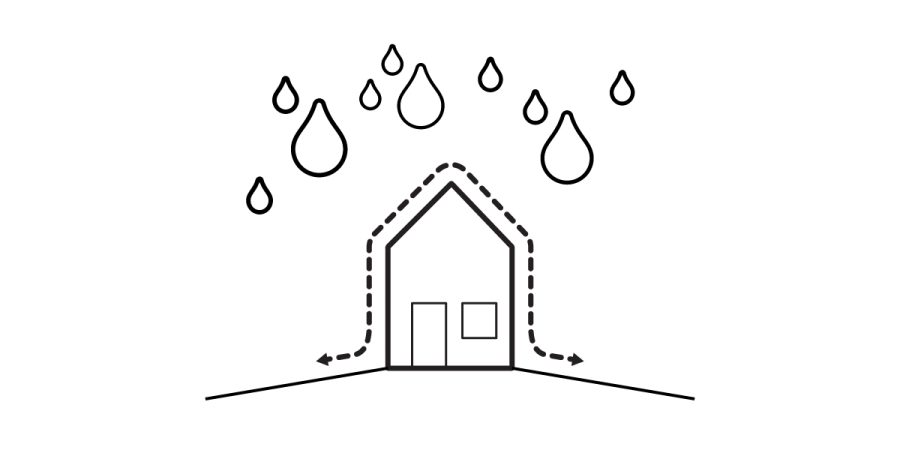
Introduction Staying dry and out of the elements is the most basic principle that architecture must fulfill. And consequently water and temperature transmission are some of the harder things buildings […]
Mass Timber (MT) Mass Timber used to be a niche product, but now is commonly considered as an option for projects. Since 2010 the growth in mass timber use has […]
Welcome to ArchOverFlow
Notice an error? Link Broken?
Have a suggestion for the next topic to be covered? Help make a better community by lettings us know. Find us here.
Register/Login to remove all ads for a better experience.