Quicklinks:
Description
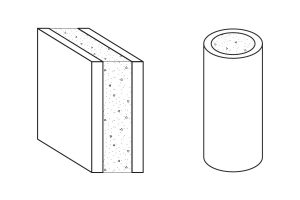
SIPs are a composite building unit consisting of two outer skins bonded to an inner core of rigid insulating material. Most SIP panels are composed of 7/16” OSB with a core of molded expanded polystyrene (EPS). Regardless, SIPS refers to essentially a sandwich of structurally sound walls that have insulation in between 2 outer faces.
- Other facing materials include plywood, aluminum, cement board, and gypsum wallboard.
- Other core materials include Extruded Polystyrene (XPS), Urethane Foam, and compressed straw.
- SIPs typically range in thickness from 4.5” to 12.5”
SIPS are precisely manufactured under factory conditions. This leads to less time on the site as the pieces are quickly assembled, and typically more precision with the factory conditions. In many situations, the SIPS factory will construct the building completely as a mock-up.
Advantages
- Decreased construction time (about one-third less than for stick-built buildings)
- Improved insulation value with no thermal bridges or reduced thermal bridging.
- Example: In 3.5” you can get R14 instead of R9.6 (fiberglass insulation)
- Reduced air infiltration. SIPS creates an air-tight building.
- Stronger than conventional stud and sheathing construction through the glued lamination and precise fittings.
- Dimension stability and flat walls for subsequent finishes
- Workers require less training in order to put together the SIPS panels.
Sustainability
SIPs require less wood than conventional houses, can use renewable resources for the facing materials, improves thermal performance, and reduces the construction waste.