Wall Assembly Thermal Gradient
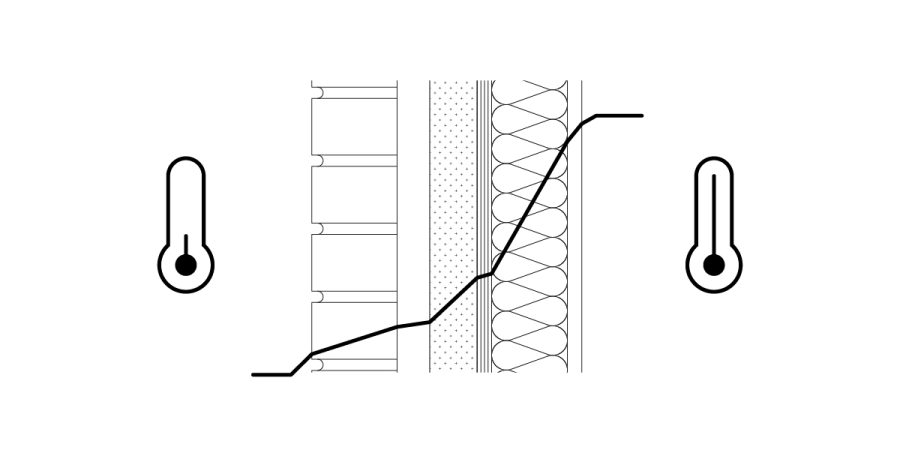
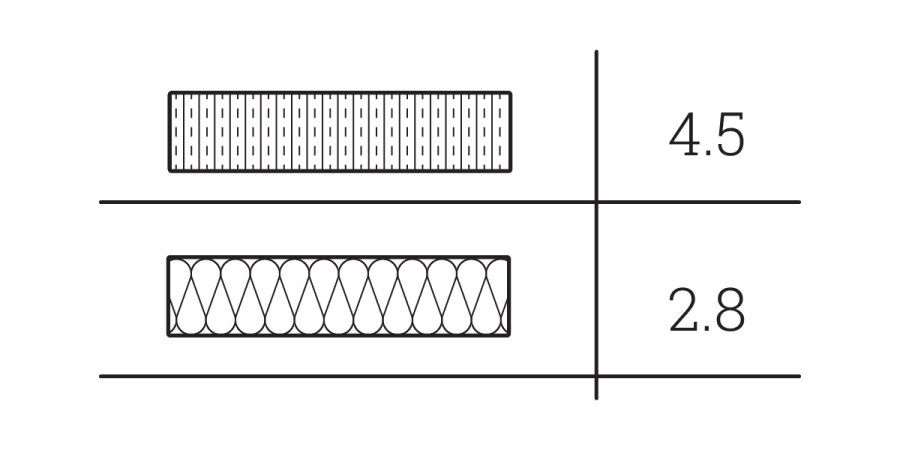
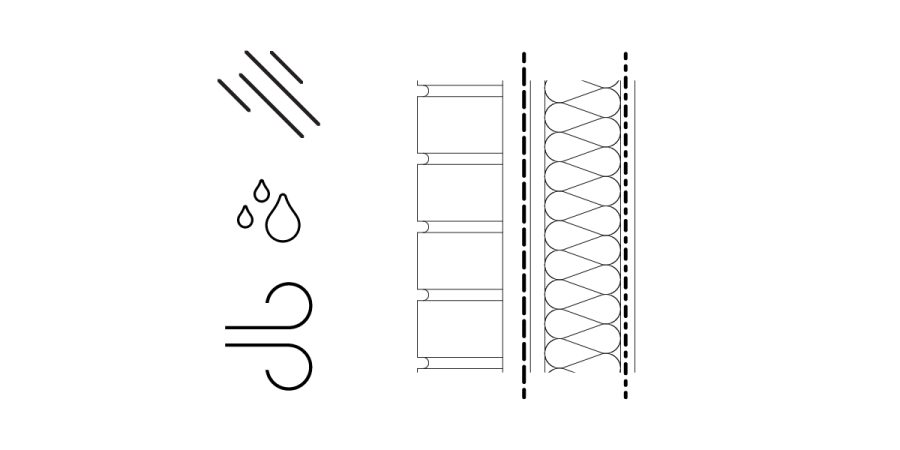
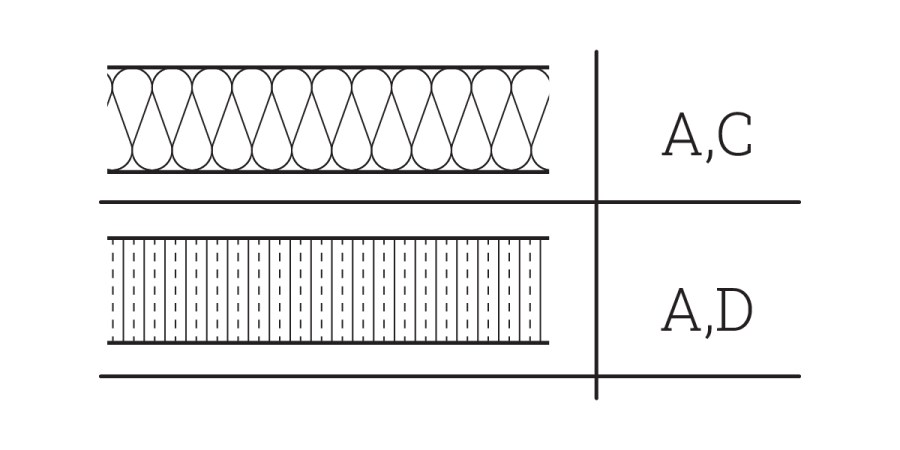
Understanding the thermal gradient within a wall assembly is crucial for effective architectural design, particularly in preventing moisture issues. This analysis involves evaluating material R-values and their impact on temperature variance, helping designers identify potential dew points. By considering factors like ASHRAE guidelines and site-specific weather, professionals can ensure assemblies meet performance requirements, even accounting for extreme conditions and internal humidity spikes.